Table of Contents
Portable generators are becoming more popular as people search for reliable power sources that can be transported easily. These generators are available in various sizes, ranging from small units suitable for camping trips to large industrial generators capable of powering entire buildings. They typically run on gasoline or propane and can supply power for several hours or even days, depending on the size of the fuel tank.
In this article, we will explore how portable generators work, the different types available, and the safety considerations that you should keep in mind when using one.
What is a Portable Generator?
When it comes to keeping your home powered up during an outage or having a reliable power source for your outdoor adventures, a portable generator is your go-to solution. Portable generators are versatile and compact powerhouses that provide a consistent power source wherever you need it.
Unlike bulky standby generators that are permanently installed, portable generators can be easily moved and used in various locations. These convenient devices are designed to power your home, campsite, or job site when grid power is unavailable or unreliable.
Understanding How Portable Generators Work
At their core, portable generators work by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. They consist of several essential parts that work together seamlessly:
- Gas or Propane Engine: The heart of the generator, the gas engine or dual fuel engine, powers the generator and produces the mechanical energy needed to generate electricity.
- Alternator: The alternator is responsible for converting the mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy.
- Voltage Regulator: To ensure a stable power output, portable generators incorporate a voltage regulator that regulates and controls the voltage level of the generated electricity.
- Control Panel: The control panel allows you to start the generator, monitor the power output, and connect appliances or devices.
Versatile Power Source
One of the key advantages of a portable generator is its ability to run on different fuel types, such as gasoline, propane, or even diesel. This flexibility enables you to choose the most suitable fuel option for your needs and availability. Additionally, portable generators come in various sizes and power outputs, allowing you to select the one that meets your specific power requirements.
Connecting the Generator
To use a portable generator, you connect it to your appliances or electrical system using extension cords or a transfer switch. This allows you to access the generator’s power when the main power source is unavailable, such as during a power outage.
In the following sections, we will explore the detailed workings of portable generators, their maintenance, and the wide range of benefits they offer in different scenarios.
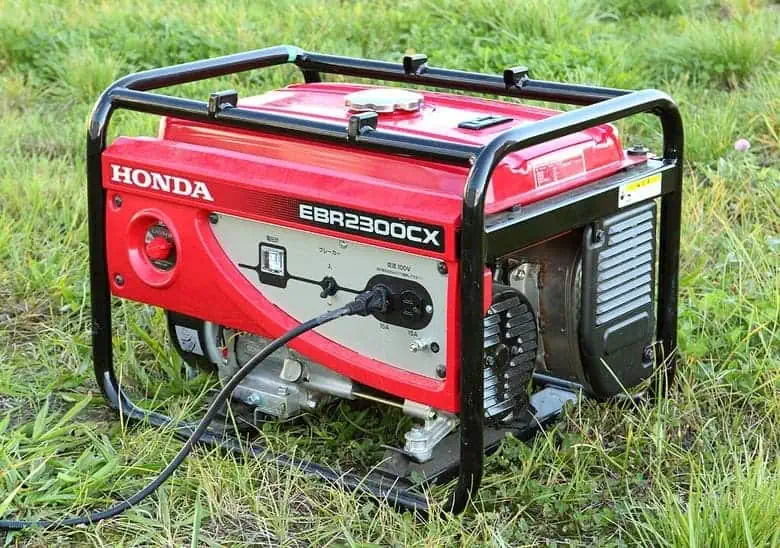
Components of a Portable Generator
To understand how a portable generator works, it’s important to familiarize yourself with its key components. Let’s take a closer look at the various parts that make up a portable generator and contribute to its efficient power generation.
Engine
The engine is the heart of the portable generator, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy. It typically runs on gasoline, propane, or diesel, and powers the generator by turning a crankshaft.
Alternator
The alternator is an essential component that converts the mechanical energy generated by the engine into electrical energy. It consists of a rotor, which spins within a stationary set of windings, creating a magnetic field that induces an electrical current.
Voltage Regulator
The voltage regulator ensures that the generator provides a consistent power source by regulating the voltage of the generated electricity. It prevents voltage spikes or drops that could damage sensitive electronics or appliances.
Control Panel
The control panel is where you interact with the portable generator. It typically includes various controls and indicators such as the start/stop switch, fuel gauge, circuit breakers, and outlets. The control panel allows you to monitor the generator’s performance and connect appliances or devices.
Fuel System
The fuel system consists of the fuel tank, fuel lines, and carburetor or fuel injectors. It delivers fuel from the tank to the engine, where it is mixed with air and ignited to generate mechanical energy.
Exhaust System
The exhaust system is responsible for safely expelling the combustion gases produced by the engine. It includes components such as the muffler and exhaust pipe, which reduce noise levels and direct the gases away from the generator.
Cooling System
To prevent the engine from overheating, portable generators are equipped with a cooling system. This system typically includes a fan, radiator, and coolant, which help dissipate the heat generated during operation.
Lubrication System
The lubrication system ensures smooth operation and prolongs the life of the generator’s internal components. It consists of an oil reservoir, pump, and filter, which distribute oil to various parts of the engine to reduce friction and wear.
Start Mechanism
Portable generators feature different start mechanisms depending on the model. They can have recoil starters, where you manually pull a cord to start the engine, or electric starters, which allow you to start the generator with the push of a button. There are also remote start generators that can be turned on from a distance with a key fob.
Wheels and Handles
Many portable generators are designed for easy mobility, thanks to wheels and handles. These features allow you to transport the generator effortlessly, whether it’s around your property or to different locations.
How Do Portable Generators Work?
Portable generators are ingenious devices that provide a reliable source of power when you need it most. But have you ever wondered how these compact powerhouses actually work? In the next lines, we’ll dive deeper into the working principles of portable generators and explore how they convert mechanical energy into electrical energy to power your home or outdoor activities.
Converting Fuel to Mechanical Energy
- Fuel Supply: To kickstart the generator, you need to supply it with the appropriate fuel, such as gasoline, propane, or diesel.
- Ignition: Once the fuel is present, the generator’s engine ignites it, creating controlled combustion within the engine’s cylinders.
- Mechanical Energy: The combustion process produces high-pressure gases that drive the piston in a reciprocating motion. This mechanical movement turns the generator’s crankshaft, which is connected to the rotor of the alternator.
Generating Electricity
- Alternator: As the rotor spins within the stationary windings of the alternator, a magnetic field is created, inducing an electrical current in the windings. This conversion of mechanical energy into electrical energy is known as electromagnetic induction.
- Voltage Regulation: The voltage regulator monitors the electrical output to ensure a consistent power source. It adjusts the generator’s output voltage to maintain a steady flow of electricity within the desired range, protecting your valuable appliances from voltage fluctuations.
Powering Your Devices
- Control Panel: The control panel of the generator allows you to connect your devices and appliances. It typically features outlets, such as standard 120V AC outlets or specialized outlets for higher power requirements.
- Power Distribution: By connecting your devices to the generator’s outlets or through an extension cord, the generated electricity can be distributed to power various appliances, tools, or electronic devices.
Safe Operation and Shutting Down
- Monitoring: While the generator is running, it’s crucial to monitor the fuel level, oil level, and overall performance. Regular checks help ensure the generator operates smoothly and prevents any potential issues.
- Shutdown: When you no longer require power or need to refuel the generator, follow the manufacturer’s instructions to safely shut it down. This process usually involves turning off the engine and allowing it to cool down before refueling.
Remember, portable generators should be operated in well-ventilated areas to prevent the accumulation of carbon monoxide gas. It’s essential to follow safety guidelines and never run a generator indoors or in confined spaces.
How to Turn On and Use a Portable Generator Properly
1. Prepare the Generator
Ensure your safety by following these steps before operating the generator:
- Read and understand the generator’s user manual thoroughly.
- Place the generator outside in a well-ventilated area, away from windows, doors, and vents. This prevents the buildup of carbon monoxide, a deadly gas produced during operation.
- Install a muffler on the generator to reduce noise pollution.
- Connect the generator to an appropriate power system or use an extension cord to connect it to your desired appliances.
2. Fuel the Generator
Depending on the type of generator, you may use various fuel sources such as gasoline, natural gas, or diesel. Follow these steps to fuel your generator safely:
- Check the fuel level and ensure there is enough fuel for your intended usage.
- If using a gasoline-powered generator, make sure you have a sufficient supply of fresh gasoline and use an approved container for refueling.
- For generators running on natural gas or propane, connect the generator to the appropriate fuel source following the manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Start the Generator
To start your generator, follow these general steps:
- Set the generator’s engine switch or knob to the “Off” position.
- Turn on the fuel supply (if applicable).
- Pull the choke (if equipped) to the appropriate setting.
- Turn the engine switch to the “On” or “Start” position.
- Pull the starter cord or press the electric starter button to start the engine.
Refer to your specific generator’s user manual for detailed instructions on starting procedures as they may vary between models.
4. Monitor and Operate the Generator
Once your generator is running, monitor its operation and follow these guidelines:
- Keep track of the fuel level and refill as necessary to ensure continuous power supply.
- Be mindful of the generator’s runtime and adhere to any recommended maintenance intervals.
- Avoid overloading the generator by exceeding its power capacity. Refer to the generator’s manual for its maximum power output.
- Use proper extension cords designed for generator use and avoid overloading them.
- Maintain a safe distance from the generator to prevent any accidents or injuries.
5. Shut Down the Generator
To safely shut down your generator, follow these steps:
- Disconnect the appliances or devices from the generator.
- Turn off and unplug all connected equipment.
- Allow the generator to run for a few minutes without load to cool down.
- Turn the generator’s engine switch to the “Off” position.
- Close the fuel valve (if applicable).
Maintaining a Portable Generator
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZYYXFDZtiNU
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure your portable generator remains in optimal condition and provides reliable power when you need it most. By following these maintenance guidelines, you can extend the lifespan of your generator and keep it operating at peak performance.
Maintenance Checklist
- Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer’s instructions and recommendations for your specific generator model. It provides valuable information on maintenance schedules, oil types, and other essential guidelines.
- Oil Change: Regularly change the engine oil according to the manufacturer’s recommended intervals or after a specified number of hours of operation. Use the correct oil type and ensure the oil level is maintained at the appropriate level.
- Air Filter: Clean or replace the air filter regularly to prevent dust and debris from clogging the engine and affecting its performance. A dirty air filter can decrease fuel efficiency and hinder airflow.
- Spark Plug: Inspect and clean the spark plug periodically, ensuring it’s free from corrosion and properly gapped. Replace the spark plug if necessary, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Fuel System: Stabilize the fuel or drain the tank and carburetor if the generator will be stored for an extended period. Stale fuel can cause engine issues. Use fuel additives as recommended to keep the fuel system clean.
- Battery Maintenance: If your generator has a battery, check its condition and ensure it’s properly charged. Clean the battery terminals and connections to prevent corrosion.
- Cooling System: Keep the generator’s cooling system clean and free from debris. Check the radiator or cooling fins for any obstructions and ensure proper airflow.
- Inspect Cables and Connections: Regularly inspect the generator’s cables, plugs, and connections for any signs of damage or wear. Ensure they are tightly secured and free from corrosion.
Safety and Storage Tips
- Always follow safety precautions and guidelines provided by the manufacturer, including proper grounding, fuel handling, and ventilation.
- Store the generator in a dry and well-ventilated area, protected from the elements. Ensure it’s positioned on a stable surface and covered to prevent dust and debris accumulation.
- Test the generator periodically to verify it starts and runs smoothly. This practice ensures it’s ready for use during an emergency.
- Keep a record of maintenance activities, including dates and performed tasks, to track the generator’s upkeep and schedule future maintenance accordingly.
By adhering to these maintenance practices, you can keep your portable generator in excellent condition, ready to provide reliable power whenever you need it.
Benefits of Portable Generators
Here are some of the key benefits of owning a portable generator:
1. Power Backup in Emergencies
During power outages caused by severe weather conditions, natural disasters, or utility failures, a portable generator can be a lifesaver. It ensures that essential appliances and systems in your home, such as refrigerators, sump pumps, lights, and communication devices, continue to function. This provides comfort, safety, and peace of mind until the utility power is restored.
2. Versatile and Portable Power Source
As the name suggests, portable generators are designed to be easily moved and transported. They come in various sizes and weights, allowing you to choose the one that suits your needs. Portable generators can be used not only at home but also in campsites, RVs, job sites, and outdoor events. They provide a convenient and reliable power source for various activities and settings.
3. Standalone Power Solution
Portable generators are standalone power solutions that do not require a connection to the power grid. This independence allows you to have power available even in remote areas where electrical infrastructure may be limited or nonexistent. It enables you to enjoy outdoor adventures, camping trips, or construction projects without sacrificing access to essential electrical devices and equipment.
4. Quick and Easy Setup
Setting up a portable generator is relatively simple and straightforward. With basic knowledge and understanding of the generator’s operation, you can quickly get it up and running. Portable generators typically come with user-friendly control panels and clear instructions, making them accessible to a wide range of users.
5. Reliable Power Source for Sensitive Electronics
Many portable generators, especially inverter generators, produce clean and stable power, making them safe for sensitive electronics like laptops, smartphones, and medical equipment. This feature is crucial during emergencies when you need to power essential electronic devices without risking damage due to power fluctuations.
6. Fuel Options and Efficiency
Portable generators offer various fuel options, including gasoline, propane, and diesel, providing flexibility and convenience. Some models even offer dual-fuel capabilities, allowing you to switch between different fuel sources based on availability or preference. Additionally, modern portable generators are designed to be fuel-efficient, maximizing runtime and reducing fuel consumption.
7. Peace of Mind
Owning a portable generator provides peace of mind, knowing that you have a reliable backup power source readily available. Whether it’s to ensure the safety and comfort of your family during emergencies or to power essential equipment at remote locations, a portable generator offers reassurance and prepares you for unforeseen circumstances.
In summary, portable generators offer versatility, convenience, and peace of mind. They are invaluable during power outages, outdoor activities, and other situations that require a reliable and portable power source. By investing in a portable generator, you gain the ability to maintain power in emergencies, stay connected, and enjoy the comforts of electricity wherever you go.
Conclusion: How Does a Portable Generator Work?
Understanding how a portable generator works empowers you to make informed decisions about using and maintaining them effectively. Consider investing in a portable generator for reliable power during emergencies and outdoor activities, and always prioritize safety and responsible usage. Make sure to read the manufacturer’s instructions, keep them well-maintained, and operate them in well-ventilated areas.